
It will move the HEAD, the working branch, to the indicated commit, and discard anything after: git reset -soft HEAD1.
#Sourcetree revert to previous commit code
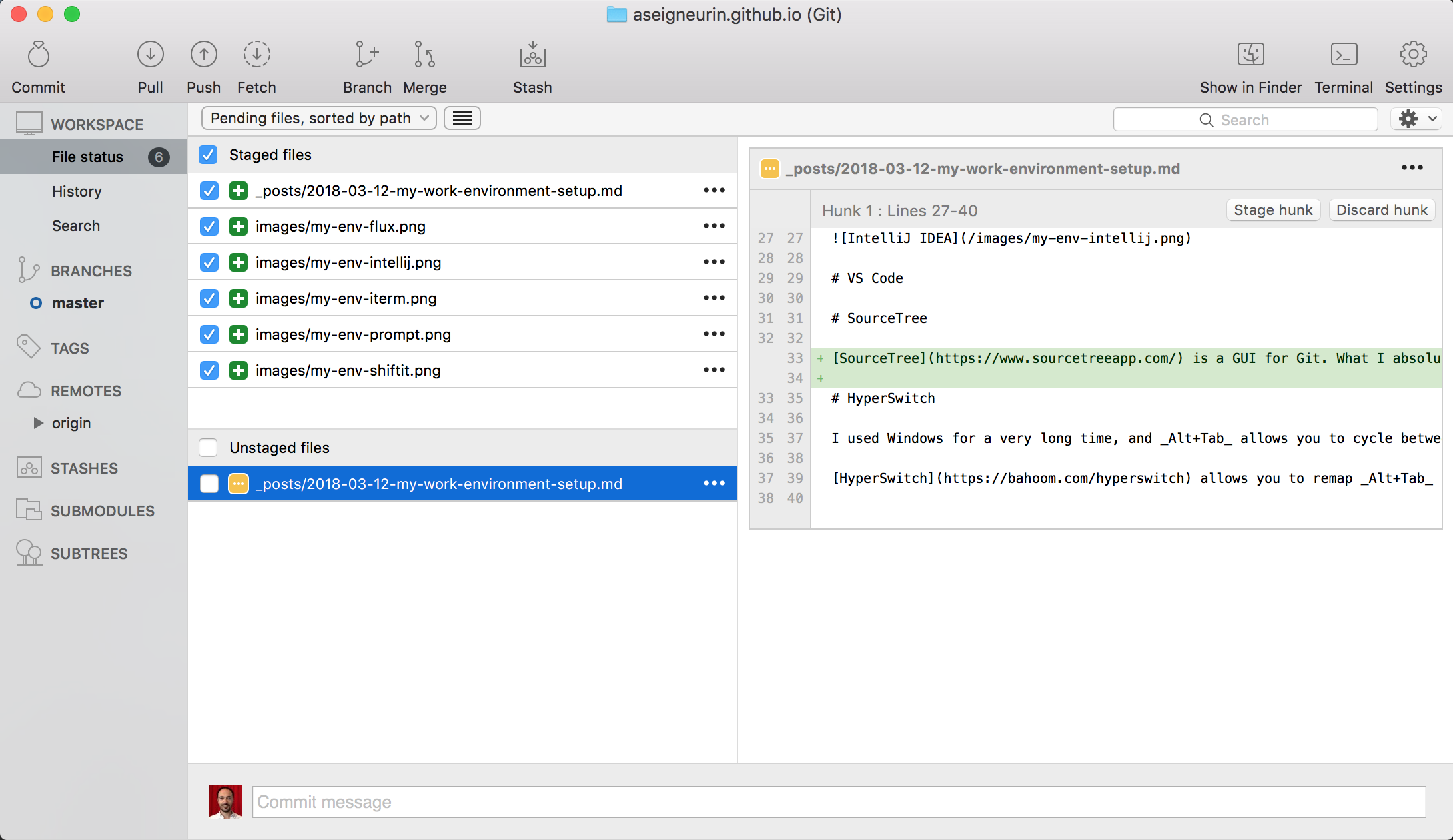
But be careful it will change the commit history, so you should use it rarely. Answer (1 of 4): In the Git and Mercurial version control systems, you can use the code amend/code option for the commit command to specify that you want to add your staged changes to the previous commit. In the example, ~ 1 refers to the number of commits backward to which the code tree will revert. Figure 1 illustrates the results for adding several commits and then reverting back one version. You can also use the reset command to undo your last commit. To start let us examine the log and find a commit to revert. Let us continue with our example from the previous section. The following section will demonstrate git revert usage. In the following example, x12345 represents the commit ID, gained from the git log output:Īlternatively, there is a shorthand method to roll back the commit: To revert commits without knowing the necessary commit ID, admins can use the command below to revert code versions relative to where the current head is. These revert commits can then be safely pushed to remote repositories to share with other developers. Normally, you use a branch name to communicate with 'git checkout'. Git then places all of that revision's files in your working copy folder. Once the IT team chooses a code version to which their tree should revert, use the commit ID to execute the command. With the 'git checkout' command, you determine which revision of your project you want to work on. To view the previous commits, use the git log –-oneline command. It resets the code tree to the version in question and deletes unstaged files.įirst, decide how far back to go into the version history. In effect, the git reset command instantiates a 'hard deletion' of all changes from now - or point-in-time of code reversion - to the designated former code commit. This command will reset everything, move the head back to the indicated commit version and remove all changes added to the code tree after that specific version number. All the files between that PIT snapshot and now are set to staged - ready to commit but not yet committed. This mode resets the code tree's head to the designated former commit instance.
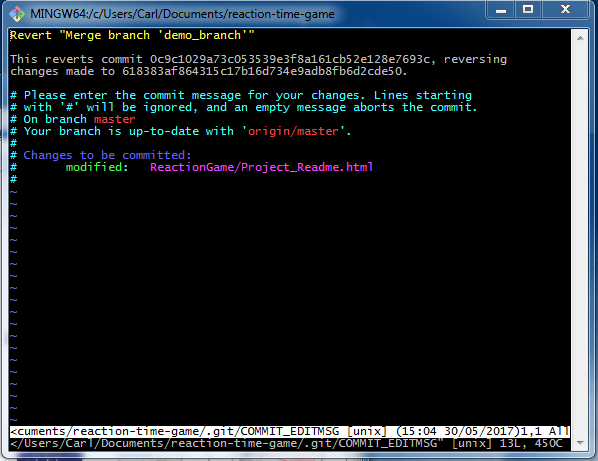
Outcomes can vary between command uses, and with which switches. One approach is the git reset command.īefore using this command, you must understand what git reset does. To illustrate example, let’s use a repository that contains “Hello world” in all languages.An administrator can roll back the code repository to a previous commit - that point-in-time copy - in several ways, depending on the end goal. To checkout a specific commit, ensure you have the repository cloned to your local machine. Let us now drill down to the bedrock of the tutorial. However, if the need arises, Git does support checking out commits. In most cases, you will want to checkout specific branches and not commits. On the other hand, Git checkout means using a specific commit as your most recent commit. However, unlike save, Git creates a specific identifier, allowing you to view or event revert to that specific save. Think of it as the instances you press save in a document. When reverting merge commits, the mainline is always the first.

After a commit is reverted, the Revert button is no longer available. In Git, a commit refers to a snapshot of a file or a collection of files in a repository. You can revert a commit from the commit details page: Similar to reverting a merge request, you can opt to revert the changes directly into the target branch or create a new merge request to revert the changes.

So, all changes made, since that commit you reset to, will still be there. Have in mind that, by default, the option -mixed is passed to git reset. When you push a commit, the safest way to revert it (rather than forcing the push with -f) is to use the revert function, so a new commit is created on top of your previous commit. This tutorial will look at reverting to a specific commit in a specific repository using the git checkout command. You will go back to the previous commit with. It allows developers to collaborate from every point of the world and revert changes to codes if need. If you want to go back to a previous commit, while keeping all of your other history, simply checkout that commit. Large companies and individual developers use it to track and share their code and projects. Git: Temporarily revert to previous commit. Git is probably the most popular and most respected version control system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
